Top 10 Benefits of Using Flexible Printed Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern electronics, the integration of innovative materials and technologies has become paramount. One such advancement is the use of flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs), which are rapidly gaining traction in various applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in the field of electronics engineering, emphasizes the significance of this technology by stating, "Flexible printed circuit boards not only enhance the functionality of devices but also contribute to their overall design and efficiency."
As electronic devices become increasingly compact and multifunctional, the need for lightweight, space-efficient solutions is more pressing than ever. Flexible printed circuit boards offer unique advantages, such as the ability to bend and twist without compromising performance, which aligns perfectly with the demands of modern design. This flexibility not only supports sophisticated product designs but also improves the reliability and lifespan of electronic devices. In this article, we will explore the top 10 benefits of using flexible printed circuit boards, shedding light on how they are revolutionizing the way we approach electronics design and manufacturing.

Benefits of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards for Compact Electronics Designs
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) have become essential in modern electronics, especially when it comes to compact design. These innovative circuits allow for greater flexibility in configuration, enabling designers to create smaller, lighter products without compromising performance. FPCBs can easily bend and twist, which is particularly beneficial for devices that require dynamic movements, such as wearables and portable gadgets. The ability to fit circuit boards into tight spaces opens up possibilities for sleek designs that adhere to contemporary aesthetic trends while maintaining functionality.
Tips for incorporating flexible printed circuit boards effectively include prioritizing the layout from the beginning stages of design. Consider the most efficient routing for components to ensure both performance and space optimization. Additionally, be mindful of the materials used; selecting high-quality substrates can enhance durability and reliability, crucial for devices exposed to varying conditions.
Another advantage of FPCBs is their potential for reduced assembly costs. By integrating multiple functions into one flexible board, manufacturers can minimize layers and connections. This consolidation not only simplifies production but also enhances the overall reliability of the device. To maximize benefits, keep in mind the importance of thorough testing during the design process, ensuring that these flexible circuits can withstand the pressures of daily use while delivering high performance.
Top 10 Benefits of Using Flexible Printed Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
| Benefit | Description | Application Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Space Saving | Flexible PCBs allow for designs that take up less physical space. | Wearable devices, smartphones |
| Lightweight | Reduced weight compared to traditional rigid boards. | Aerospace, portable electronics |
| Design Flexibility | Flexibility in design enables complex routing and shapes. | Consumer electronics, medical devices |
| Durability | Resistant to vibrations and mechanical stress. | Automotive, industrial applications |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs for complex two or three-dimensional layouts. | Mass production devices |
| Enhanced Performance | Improved electrical performance due to shorter connections. | High-frequency electronics, RF applications |
| Thermal Management | Better heat dissipation capabilities. | LED lighting, power electronics |
| Design Reduction | Fewer components and interconnections needed. | Compact devices, IoT applications |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. | Outdoor electronics, medical sensors |
| Streamlined Assembly | Easier and faster manufacturing and assembly processes. | Consumer gadgets, smartphones |
Improvement in Reliability and Durability of Modern Electronic Devices
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) have revolutionized modern electronics by enhancing the reliability and durability of devices. Their unique construction allows for better stress distribution and flexibility, reducing the chances of breakage during both manufacturing and use. Unlike traditional rigid boards, FPCBs can be bent and folded, accommodating various design configurations without compromising integrity. This adaptability ensures that these circuits can withstand the rigors of daily use, particularly in compact or mobile devices where space is at a premium.
Moreover, the materials used in FPCBs contribute significantly to their durability. These boards are typically made from polyimide or other robust polymers that offer excellent resistance to temperature fluctuations, moisture, and chemicals. This resilience makes FPCBs ideal for environments where traditional circuit boards would fail, such as in automotive or medical applications. The ability to endure harsh conditions not only extends the lifespan of the devices but also enhances their overall performance, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions that could disrupt critical functions or lead to costly replacements.
Cost-Effectiveness of Manufacturing Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs) have surged in popularity within the electronics industry due to their remarkable cost-effectiveness in manufacturing. According to a report by IDTechEx, the flexible electronics market is anticipated to reach a staggering $40 billion by 2025, showcasing a strong demand for FPCBs driven by their lightweight and adaptable characteristics. The streamlined production process reduces material waste and allows manufacturers to create complex designs without incurring significant extra costs, making FPCBs a financially savvy choice for both startups and established companies.
In addition to lower production costs, FPCBs offer manufacturing advantages such as simplified assembly and reduced assembly times. For instance, the use of FPCBs can decrease the number of interconnections needed, which not only minimizes the risk of failure but also shortens the overall time to market. Research from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) highlights that companies utilizing flexible circuits can realize a 30% reduction in assembly time compared to traditional rigid PCB alternatives.
Tips: When considering FPCBs for your projects, ensure to evaluate the long-term savings on both material and assembly costs. Additionally, take advantage of FPCB designs that allow for multi-layer configurations to maximize functionality while minimizing space. Embracing innovative manufacturing techniques could yield significant financial benefits and enhance your product's competitive edge in the rapidly evolving electronics landscape.
Top 10 Benefits of Using Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
Enhanced Thermal Management for High-Performance Applications
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) have revolutionized the landscape of modern electronics, particularly in their ability to enhance thermal management in high-performance applications. The unique design of FPCBs allows for better heat dissipation, ensuring that electronic components function efficiently under varying conditions. By allowing for a more versatile layout, these boards enable designers to position heat-sensitive components away from heat-generating elements, thereby reducing the risk of thermal overload and ensuring the longevity of devices.
Moreover, FPCBs can be tailored with specific materials that possess excellent thermal conductivity, further improving heat distribution across the board. This optimization is crucial in high-performance applications, such as in computer processors or advanced communication devices, where even slight temperature fluctuations can lead to performance degradation. The ability to manage thermal issues effectively not only enhances device reliability but also potentially lowers cooling system requirements, leading to more compact and energy-efficient designs. In today’s fast-paced technological environment, the enhanced thermal management capabilities of flexible printed circuit boards are indispensable for achieving optimal performance and reliability in cutting-edge electronic devices.
Increased Design Flexibility and Integration Capabilities in Electronics
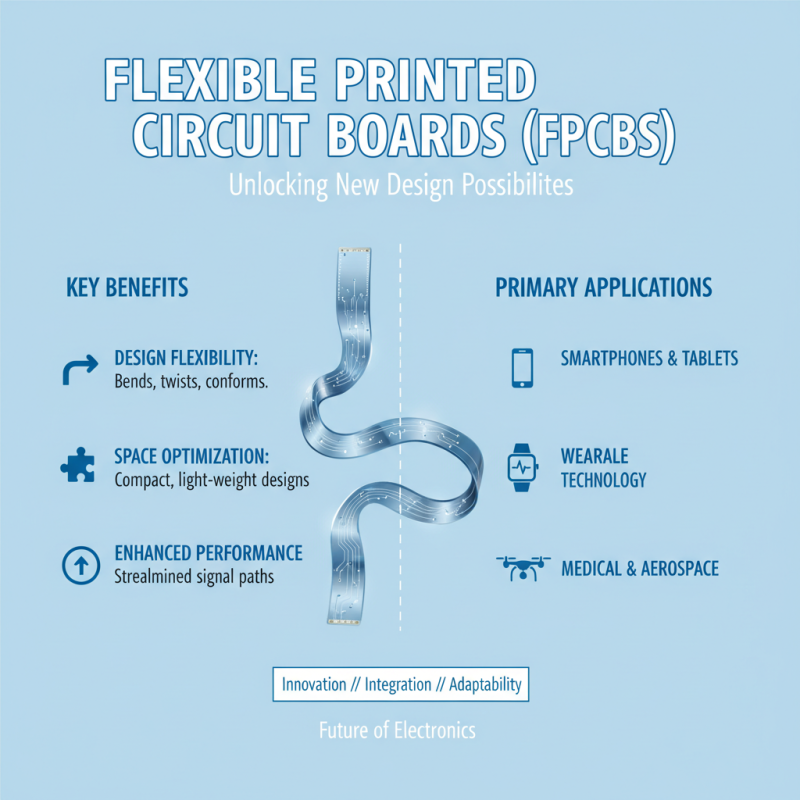
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs) have revolutionized the landscape of modern electronics, offering unparalleled design flexibility and integration capabilities. Unlike traditional rigid circuit boards, flexible circuits can bend, twist, and conform to the space restrictions of compact electronic devices. This adaptability allows engineers to create innovative designs that maximize performance while minimizing size and weight, making FPCBs ideal for applications ranging from smartphones to wearable technology. Their ability to fit into tight spaces and navigate complex geometries significantly enhances product development possibilities, enabling designers to push the boundaries of conventional electronics.
Moreover, the integration capabilities of flexible circuit boards enhance overall functionality by allowing multiple electronic components to be combined into a single flexible substrate. This integration not only streamlines the manufacturing process but also reduces assembly time and costs. By consolidating multiple functions into one compact unit, designers can create more reliable and efficient electronics that are not only lighter but also more robust against physical stress. These advantages have made FPCBs a crucial component in the evolution of modern electronics, facilitating the creation of cutting-edge devices that meet the increasing demand for advanced functionality and portability.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Printed PCB Board Insights: Trends, Market Value & Manufacturing Innovations in 2023
-
The Future of Electronics: How Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are Revolutionizing Device Design
-
2025 Strategies for PCB Prototyping to Improve Product Development Efficiency
-

2025 Top Trends in Printed PCB Board Technology and Innovations You Need to Know
-
10 Essential Tips for Designing High-Quality PCB Flex Circuits
-

10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs