Top 10 Benefits of Rigid Flex PCB for Electronics Design?
Rigid flex PCBs are transforming the electronics design industry. According to a recent market report by IPC, the global demand for rigid flex PCBs is expected to grow by over 12% annually. This growth is fueled by the increasing complexity of modern electronics, especially in sectors like aerospace and medical devices. These PCBs offer unparalleled design flexibility, helping engineers to create compact, lightweight solutions.
Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in PCB technology, emphasizes the potential of rigid flex PCBs. She states, “The key advantage of rigid flex PCBs lies in their ability to combine the benefits of both rigid and flexible circuits.” However, despite their advantages, some designers still struggle with implementation. Design difficulties can arise, often due to a lack of familiarity with the technology. Understanding these challenges is crucial for optimizing the design process in electronics.
With the right knowledge, designers can fully leverage rigid flex PCBs. Incorporating these technologies can lead to innovative products that stand out in the competitive market. Nonetheless, the learning curve remains a challenge for many. Continuous education and adaptation are essential to keep pace with industry advancements.

Overview of Rigid Flex PCB Technology in Electronics Design
Rigid flex PCBs combine the flexibility of a flexible PCB with the durability of a rigid PCB. This innovation allows for intricate designs in compact spaces. Designers can create complex circuits with fewer interconnections. This leads to greater reliability and reduces the risk of failure. Many people overlook the intricacies involved in their production. Each layer must be meticulously crafted to ensure functionality and integrity.
The integration of rigid and flexible materials can pose challenges. It requires careful consideration in the design phase. Designers must account for stress points where the flex meets the rigidity. This adds complexity to the development process. Mistakes in this phase can result in significant costs and delays. Additionally, while rigid flex PCBs offer many advantages, not all projects should use them. For simpler applications, traditional boards may suffice, highlighting the importance of thoughtful design choices. Balancing these factors is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Top 10 Benefits of Rigid Flex PCB for Electronics Design
Enhanced Durability and Flexibility Compared to Traditional PCBs
Rigid flex PCBs have gained attention in electronics design due to their remarkable durability and flexibility. Unlike traditional PCBs, they combine the advantages of both rigid and flexible circuits. According to a recent industry report, the use of rigid flex PCBs can reduce overall product weight by 50%. This not only enhances portability but also improves heat dissipation, which is crucial for high-performance devices.
The flexibility of these PCBs allows for unique configurations in tight spaces. This is important for modern electronics, which often have limited real estate. Flexibility can also lead to fewer interconnections. Fewer interconnections mean decreased chances of failure. Nevertheless, designing rigid flex PCBs can present challenges. Engineers must carefully consider the trade-offs between durability and flexibility.
Manufacturers have reported that while rigid flex PCBs are more resistant to mechanical stress, they can be more complex to assemble. Specialized tools and processes are often required. A study indicated that 30% of engineers face difficulties with the initial design phase. This complexity can lead to increased time and costs. Yet, the long-term benefits often outweigh these initial hurdles.
Improved Performance in Space-Constrained Applications
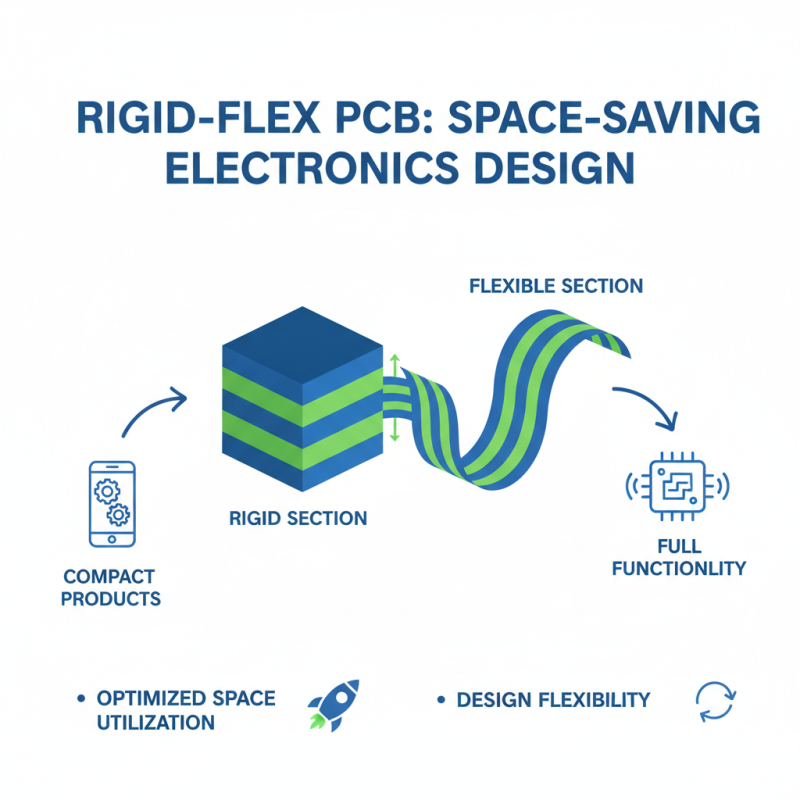
Rigid Flex PCB has gained popularity in electronics design, especially for space-constrained applications. Its unique structure combines both rigid and flexible elements, enabling more efficient use of available space. This design flexibility allows engineers to create compact products without compromising functionality.
In applications like wearable technology or compact medical devices, every millimeter counts. Rigid Flex PCBs offer an innovative solution by fitting neatly into tight areas. They can bend and fold, making intricate designs possible. However, this approach may complicate manufacturing processes. Adapting machinery and techniques to accommodate these designs can be challenging.
Designers often face trade-offs when using Rigid Flex PCBs. They provide improved durability, but the costs might increase. Achieving the right balance between performance and budget is crucial. As manufacturers become more skilled in this area, new techniques will emerge. We may still see hiccups in production, requiring continuous improvements.
Reduced Weight and Size Benefits for Portable Devices
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have revolutionized electronics design, especially in portable devices. One key advantage is their reduced weight. Rigid flex PCBs can be up to 70% lighter than traditional circuit boards. This significant reduction enhances portability, making devices easier to carry.
The compact nature of rigid flex PCBs is another major benefit. They save space, allowing designers to create slimmer devices. A recent industry report indicates that miniaturization in electronics has increased by 35% in the last decade. This trend is crucial for smartphones, wearables, and other compact gadgets.
Tip: Prioritize space-saving designs in your projects. Embrace the use of multi-layer rigid flex PCBs when possible. Consider potential limitations in design complexity that might arise with ultra-thin materials. Be mindful of the balance between flex capability and durability.
The lightweight trend can sometimes result in less robust devices. That’s a concern for users. Understanding the trade-off between weight and performance is essential. Always aim for a harmonious mix to provide the best user experience.
Cost-Effectiveness in High-Volume Electronics Manufacturing
Rigid flex PCBs are increasingly popular in electronics design. One major advantage is their cost-effectiveness in high-volume manufacturing. By combining flexible and rigid features, they streamline the assembly process. This reduces labor costs. Consequently, manufacturers can produce more units in less time.
Moreover, rigid flex PCBs save space. They allow for complex circuit layouts in compact designs. This can minimize material costs and save on shipping expenses. However, designers must be cautious. The initial setup costs for rigid flex manufacturing may be high. This can deter small projects. Still, for large scale production, the overall savings often outweigh the initial investment.
Flexibility in design is another point to consider. Rigid flex PCBs can adapt to various electronic applications. This creates opportunities for innovative solutions. Yet, the learning curve might be steep for new users. Understanding the best practices for design and assembly is crucial. Mistakes in the early stages could lead to increased costs or delays.
Related Posts
-

2026 Top Rigid Flex Technology Trends You Need to Know?
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Printed PCB Boards for Your Electronics Projects
-

What is a Flex Circuit? Benefits, Applications, and Key Considerations Explained
-

Top 10 Printed PCB Board Insights: Trends, Market Value & Manufacturing Innovations in 2023
-

2025 Top Trends in Printed PCB Board Technology and Innovations You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Best Printed Circuits Designs for Electronics in 2023