10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs
The advancement of PCB flex technology has transformed the landscape of electronic design, enabling engineers to create more compact, lightweight, and efficient devices. According to a recent report by the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits), the flexible printed circuit board market is expected to reach $25 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10% from 2020. This remarkable growth is driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics, wearable devices, and IoT applications, where space-saving and flexibility are paramount.
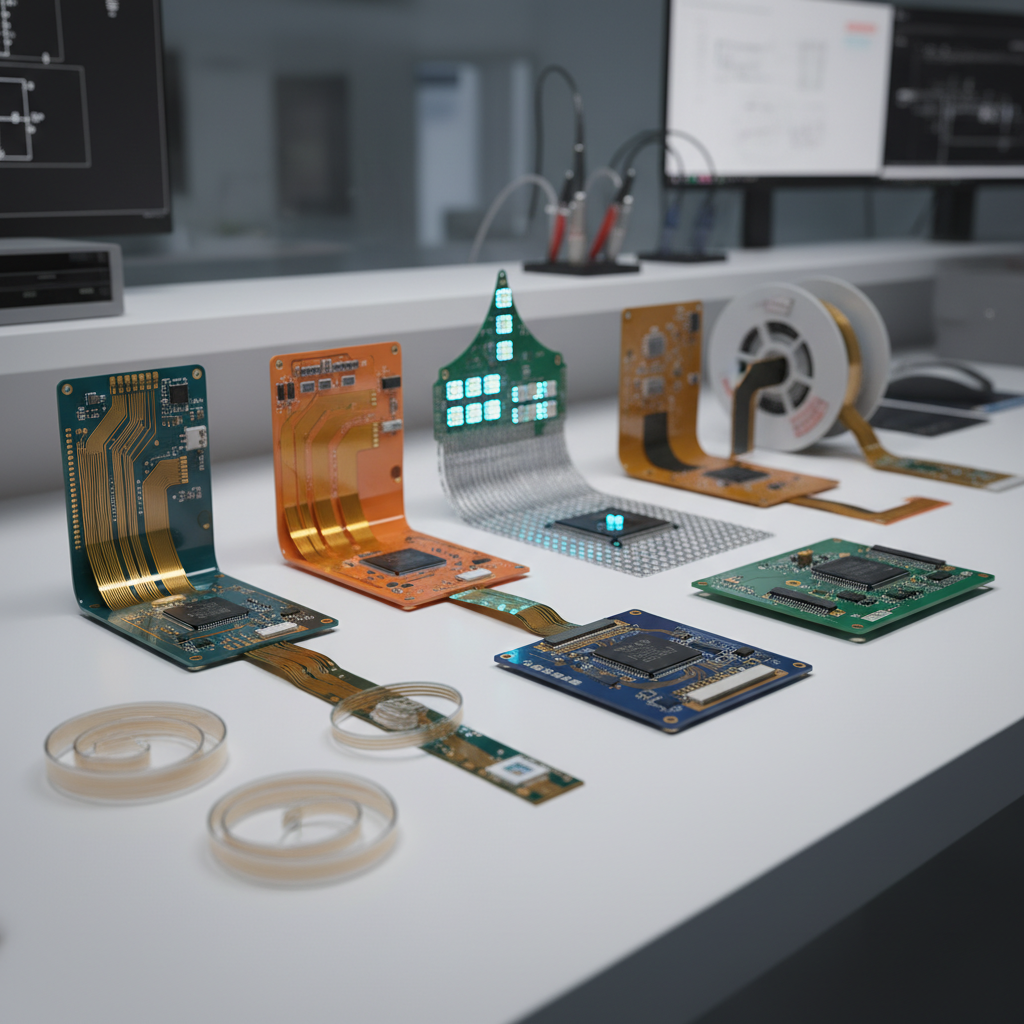

Industry experts highlight the significance of integrating the best PCB flex technologies into electronic designs. As Dr. John S. Thompson, a leading researcher in flexible electronics, noted, "The future of electronics lies in our ability to innovate with flexibility; PCB flex technologies not only enhance performance but also pave the way for next-generation devices." The amalgamation of innovative materials, manufacturing processes, and design strategies contributes to this burgeoning field, proving essential for businesses striving to remain competitive in today's fast-paced market.
In this article, we will explore the ten best PCB flex technologies that are set to redefine electronic designs, showcasing how they can be utilized to enhance functionality, reduce weight, and improve overall device performance. Whether you're a seasoned engineer or a newcomer to the field, understanding these technologies is crucial for achieving success in your electronic design endeavors.
Introduction to PCB Flex Technologies in Electronic Design

Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have revolutionized the landscape of electronic design by offering adaptability and space-saving advantages that rigid boards cannot provide. As electronic devices become more intricate and compact, the demand for innovative PCB flex technologies continues to grow. These advancements not only enhance the functionality of devices but also facilitate intricate designs that can conform to various shapes and sizes, allowing for greater creativity in product development.
Emerging PCB flex technologies harness materials and manufacturing processes that optimize performance and durability. Techniques such as sequential lamination, flexible copper cladding, and advanced thermal management pave the way for high-density interconnections and improved signal integrity. Integrating these flex technologies into electronic designs enables engineers to overcome traditional limitations, leading to smarter and more efficient products that can withstand environmental stresses while maintaining design integrity.
As the future of electronics shifts towards more compact and versatile applications, understanding and leveraging these PCB flex technologies will be crucial for successful product innovation.
Key Advantages of Using Flexible PCBs in Electronics
Flexible printed circuits (PCBs) have revolutionized the electronic design landscape, offering unique advantages that traditional rigid PCBs cannot match. One of the key benefits of using flexible PCBs is their ability to save space in compact electronic devices. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the flexible PCB market is projected to reach USD 32 billion by 2025, indicating a growing demand for lightweight and space-efficient solutions. This flexibility enables engineers to design intricate and innovative layouts that accommodate modern technological requirements, particularly in sectors like consumer electronics and medical devices.
Another significant advantage of flexible PCBs is their durability and resistance to environmental stressors. Flexible circuits are less prone to damage from vibrations and thermal fluctuations, which is essential for devices operating in challenging conditions. A study from IPC found that flexible circuits can achieve a lifespan that is 2-3 times longer than that of traditional PCBs under similar mechanical and thermal stress. This longevity not only enhances reliability but also contributes to reduced maintenance costs and improved overall performance in various applications. The integration of flexible PCBs in electronic designs is thus a critical factor in meeting the demands of today's advanced technology.
Types of Flex Technologies for PCB Manufacturing
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have revolutionized electronic design by allowing for greater versatility and compactness in various applications. There are several types of flex technologies used in PCB manufacturing that can significantly enhance performance and reliability. One popular type is the polyimide flex circuit, known for its thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature environments. Another widely utilized technology is the polyester-based flex circuit, which is generally cost-effective and easier to process, ideal for less demanding applications.
Moreover, the build-up flex technology allows for multi-layered designs while maintaining flexibility, providing designers the capability to create complex circuits in a thinner profile. Additionally, there are rigid-flex designs that combine rigid and flexible elements, enabling innovative applications in devices with tight spatial constraints. As electronic devices continue to become more compact and multifunctional, exploring various flex technologies in PCB manufacturing will be essential for achieving optimal design solutions.
Comparison of Flex Technologies for PCB Manufacturing
Design Considerations for Implementing Flexible PCBs
When considering the implementation of flexible PCBs (FPCs), designers must be aware of various critical factors that significantly influence both performance and usability. A recent study highlights the importance of mathematical modeling in optimizing flexible printed circuit configurations, addressing the challenges of deformation and enhancing design integrity. Flexible PCBs can bend and conform to various shapes, which is essential in modern electronic devices where space is often limited. According to industry reports, the global flexible PCB market is projected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand in consumer electronics, particularly in smartphones and wearables, where miniaturization is key.
Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing of conductive materials, offer new avenues for developing more intricate and effective designs. Research conducted at Dalian University of Technology demonstrates how freestanding 3D conductive wires can be produced, facilitating the creation of lightweight and highly flexible circuit layouts. In tandem with innovations in design techniques, such as those needed for high-speed interconnects, embracing flexible PCB technology can lead to improved signal quality and reduced issues like cross-talk. As electronic designs continue to evolve, these considerations will be pivotal in enhancing both functionality and performance.
10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs
| Technology | Material Type | Layer Count | Thickness | Temperature Rating | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide Flex Circuits | Polyimide | 1-8 Layers | 0.001" - 0.010" | Up to 260°C | Highly Flexible |
| PET Flexible PCB | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | 1-4 Layers | 0.002" - 0.010" | Up to 150°C | Moderately Flexible |
| Bendable Circuit | FR-4 | 1-6 Layers | 0.003" - 0.020" | Up to 130°C | Limited Flexibility |
| Flexible Hybrid Electronics | Various | Varied | Varied | Dependent on materials | Highly Flexible |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Hybrid (Rigid and Flex materials) | Multiple Configurations | Varied | Up to 125°C | Variable Flexibility |
Future Trends and Innovations in PCB Flex Technologies
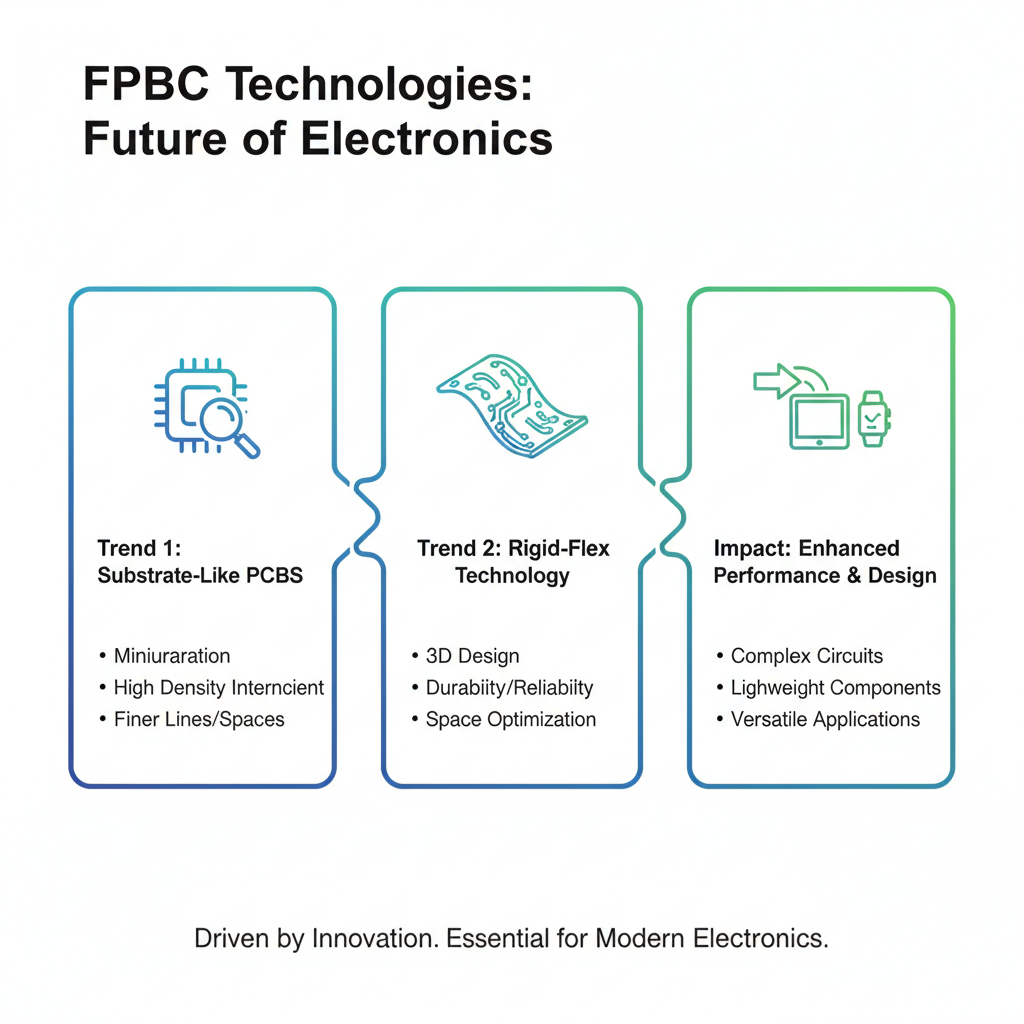
Flexible printed circuit board (FPCB) technologies are rapidly transforming the electronics landscape, with numerous innovations poised to drive future growth. As industries increasingly rely on lightweight, compact components, trends in FPCB design and manufacturing are becoming critical. The shift towards Substrate-Like PCBs and Rigid-Flex technology signifies a major leap in performance, allowing for more complex circuit designs while optimizing space and enhancing durability. This transformation is not merely a trend but an essential evolution to meet the demands of modern electronic applications.
Tips: When designing flexible PCBs, consider the mechanical constraints of your application. The choice of materials can significantly influence both flexibility and electrical performance. Additionally, integrating bio-microsystem technologies can pave the way for innovative healthcare solutions, marking a pivotal point in lab-on-a-chip development. As you keep an eye on emerging trends, collaborating with startups focusing on sustainable manufacturing can provide a competitive edge in sustainability and innovation.
The continuous growth of the PCB market, particularly in sectors emphasizing flexibility and adaptability, underscores the importance of staying ahead of industry advancements. By leveraging insights from startups and engaging with evolving technologies, designers can enhance their operations and meet the ever-changing needs of the electronic design space.
Related Posts
-
10 Essential Tips for Designing High-Quality PCB Flex Circuits
-
2025 Strategies for PCB Prototyping to Improve Product Development Efficiency
-

Top 10 Printed Boards: Best Options for Quality and Performance in 2023
-

Top 10 Printed PCB Board Insights: Trends, Market Value & Manufacturing Innovations in 2023
-
Exploring the Advantages of Aluminum PCBs in Modern Electronic Design: A Complete Guide
-

How to Choose the Best LED Circuit Board for Maximum Efficiency: Key Factors and Industry Insights