2025 How to Choose the Right Flex Printed Circuit Board for Your Needs
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics, the significance of selecting the right flex printed circuit board (FPCB) cannot be overstated. According to Dr. William Hughes, a leading expert in flexible electronics, "The choice of the appropriate flex printed circuit board is crucial to ensure both performance and reliability in modern devices." This statement underscores the importance of understanding various factors such as material composition, manufacturing techniques, and application-specific requirements when making a decision about FPCBs.
Flex printed circuit boards are not just about connectivity; they represent a convergence of functionality and versatility that caters to the increasing demand for compact and lightweight electronic solutions. As devices become smaller and more complex, FPCBs offer the flexibility needed to navigate intricate designs while maintaining essential electrical performance.
Choosing the right flex printed circuit board involves careful consideration of dimensions, layers, and environmental conditions, making it imperative for engineers and designers to be well-informed. With the right knowledge and guidance from industry experts, stakeholders can make informed decisions that propel their projects towards success and innovation.
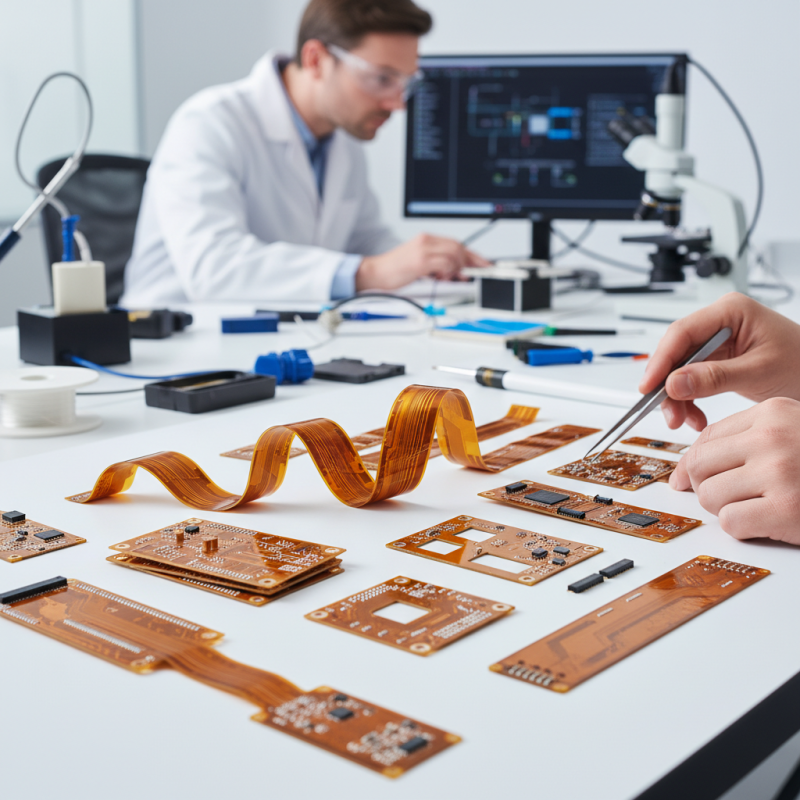

Understanding Flex Printed Circuit Boards: Types and Applications
Flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) have gained significant traction in various industries due to their versatile applications and advantages over traditional rigid boards. These boards come in different types, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer designs, each catering to specific requirements. According to a recent industry report from MarketsandMarkets, the global flex PCB market is expected to reach $26.78 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 9.3%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and compact electronic devices.
When considering the right flex PCB for your needs, it's essential to understand their various applications. They are widely used in consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive systems, and aerospace technology. For example, their ability to conform to complex shapes makes them ideal for wearables, while their reliability in extreme environments suits aerospace and defense applications. Additionally, as technology advances, the integration of flex PCBs in the Internet of Things (IoT) devices continues to rise, showcasing their importance in supporting smart connectivity.
**Tips:** When selecting a flex PCB, consider the following: assess the flexibility and durability required for your application, as some projects may demand high bendability while others may prioritize thermal or mechanical stability. Also, evaluate the material options—polyimide and polyester being the most common, each suited to different environmental conditions. Finally, always factor in the manufacturing capabilities of your supplier to ensure they can meet your specific design needs efficiently.
2025 How to Choose the Right Flex Printed Circuit Board for Your Needs - Understanding Flex Printed Circuit Boards: Types and Applications
| Type | Material | Application | Thickness | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-sided Flex | Polyimide | Consumer Electronics | 0.1 mm | High |
| Double-sided Flex | Polyimide | Medical Devices | 0.2 mm | Medium |
| Rigid-Flex | FR-4 | Aerospace | 0.4 mm | Variable |
| Multi-layer Flex | Polyimide | Telecommunications | 0.3 mm | High |
| Sensor Flex | Polyester | Automotive | 0.05 mm | Very High |
Key Factors in Selecting Flex Printed Circuit Boards for Your Project
When selecting flex printed circuit boards (FPCBs) for your project, several key factors must be considered to ensure that the board meets your specific requirements. One of the most critical aspects is the material selection. Flexible PCBs are typically made from materials such as polyimide and polyester, which offer varying degrees of flexibility, thermal stability, and dielectric strength. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for flexible printed circuit boards is projected to reach approximately $20 billion by 2025, underscoring the increasing demand for high-performance materials that can withstand the rigors of modern electronics.
Another important factor is the design and layout of the FPCB. The complexity of your circuit design will affect the choice of layout and the type of connections you need. High-density interconnections (HDI) are becoming standard in many applications, providing more functionality in smaller spaces. A study by IPC indicated that approximately 60% of designers plan to incorporate HDI in their next projects due to benefits like reduced size and improved performance. Additionally, considering the manufacturing techniques available is crucial, as this will impact the overall cost and time-to-market for your product. Balancing these elements effectively will ensure that the chosen flex printed circuit board not only meets the technical specifications but also aligns with your project’s budget and timeline.
Material Selection: Comparing Polyimide vs. Polyester in Flex PCBs
When choosing the right flex printed circuit board (PCB) for your specific applications, material selection plays a critical role. Among the most commonly used materials in flex PCBs are polyimide and polyester, each offering distinct advantages and characteristics. Polyimide is recognized for its superior thermal stability, flexibility, and resistance to harsh environments, making it an excellent choice for high-performance applications, such as aerospace or medical devices. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures and its excellent dielectric properties further enhance its suitability for complex electronic designs.
On the other hand, polyester presents a more cost-effective alternative with good mechanical strength and moderate flexibility. While it may not match polyimide in terms of thermal performance, polyester flex PCBs are often favored for applications that do not require extreme temperature resistance. They are commonly used in consumer electronics, where cost considerations are paramount, and less demanding conditions prevail. Analyzing the specific requirements of your application—such as the desired thermal stability, flexibility, and budget—will help guide the choice between these two materials, ensuring the most effective performance of your flex PCB design.
Material Selection Comparison: Polyimide vs. Polyester in Flex PCBs
Industry Standards and Reliability Testing for Flex Printed Circuit Boards
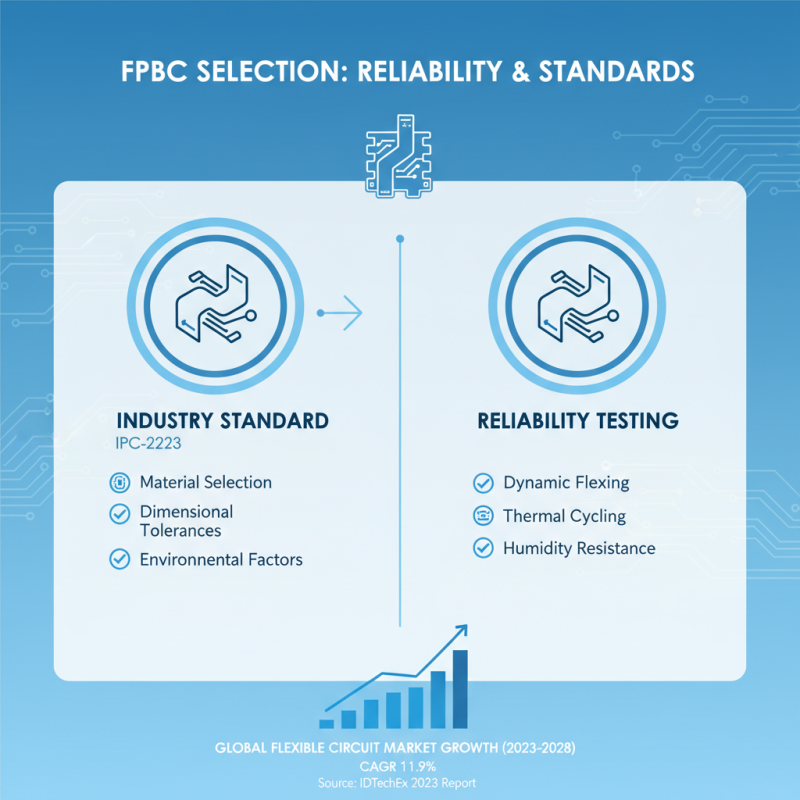
When selecting a flex printed circuit board (FPCB), understanding industry standards and reliability testing is crucial for ensuring that the board meets application-specific requirements. The IPC-2223 standard outlines design specifications for flexible circuits, emphasizing factors such as material selection, dimensional tolerances, and environmental considerations. This standard guides manufacturers in producing FPCBs that can withstand the rigors of dynamic applications while maintaining functionality. According to a 2023 report by IDTechEx, the global flexible circuit market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.9%, underscoring the increasing reliance on these versatile components in the electronics industry.
Reliability testing is another vital aspect of evaluating FPCBs. Common tests include thermal cycling, bend testing, and tensile strength evaluation, which help determine a board's performance under various conditions. A study published by the IEEE highlighted that FPCBs subjected to accelerated life testing demonstrated a failure rate of only 0.2% over a 2,000-cycle lifespan when manufactured according to stringent industry standards. This data reflects the importance of adhering to established protocols to ensure both performance and longevity. When selecting an FPCB, considering these testing methodologies, along with compliance to industry standards, is key to making an informed decision that aligns with specific project requirements.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Flex Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing
When budgeting for flex printed circuit board (FPCB) manufacturing, it’s crucial to understand the various cost factors involved. According to a report from IPC, the global flex circuit market is projected to reach approximately $20 billion by 2025, underscoring the relevance of accurate cost assessments in this competitive landscape. Costs can vary significantly based on factors such as material specifications, layer counts, size, and complexity of the design. For instance, high-density interconnect (HDI) flex circuits typically command higher prices due to the intricate manufacturing processes involved, which can increase production costs by up to 30% compared to standard options.
In addition to raw materials, companies must also consider tooling, labor, and regulatory compliance costs when calculating their budgets. A study by TechSearch International highlights that tooling expenses can represent up to 20% of total FPCB costs, particularly for custom designs. Furthermore, ensuring compliance with industry standards can add a layer of expense, as manufacturers might need to invest in certifications, which can cost anywhere from $5,000 to $50,000, depending on the requirements. Therefore, companies should conduct a thorough cost analysis to ensure they allocate adequate resources to both initial manufacturing and potential future modifications, thereby maximizing their return on investment in flex printed circuit technology.
Related Posts
-

10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs
-
10 Essential Tips for Designing High-Quality PCB Flex Circuits
-
2025 Strategies for PCB Prototyping to Improve Product Development Efficiency
-
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development
-

2025 Guide: How to Master PCB Design for Innovative Electronics Projects
-
What is a LED Circuit Board and How Does it Work in Electronics