Top Tips for Choosing the Right PC Boards for Your Needs?
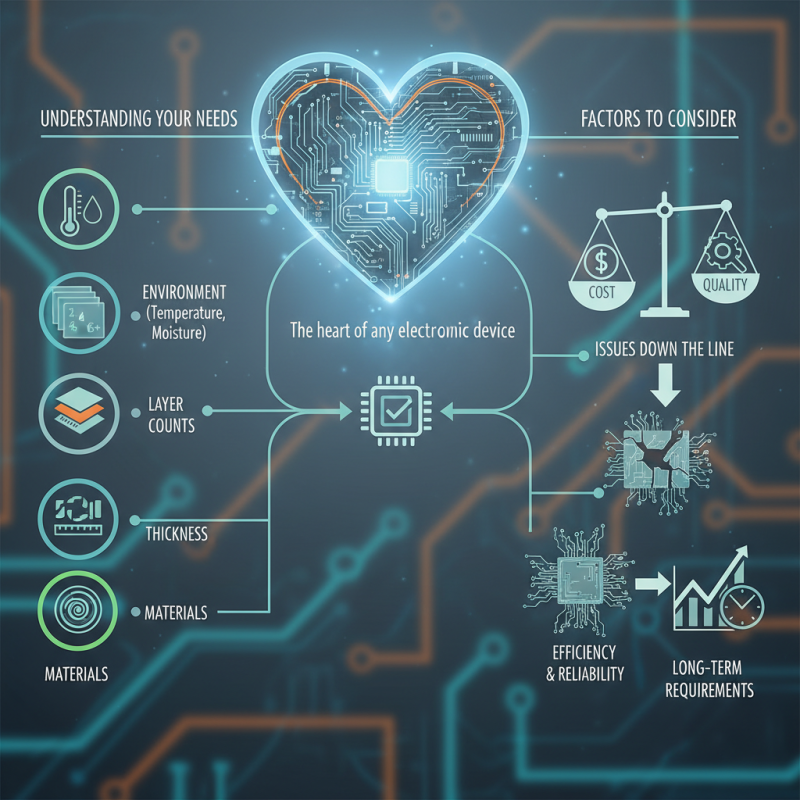
Choosing the right PC boards is crucial for any electronics project. According to Dr. Angela Martinez, a leading expert in the field, "The heart of any electronic device lies in its PCB." This highlights the significance of understanding your specific needs before selecting a board.
When it comes to PC boards, various factors come into play. Each project has unique requirements. Materials, thickness, and layer counts are just a few aspects that can affect performance. Make sure to consider the environment in which the PCB will operate. Temperature and exposure to moisture can impact longevity.
Yet, it's easy to overlook essential details. Sometimes, the cost takes priority over quality, which can lead to issues down the line. Every choice you make with PC boards shapes your project's efficiency and reliability. Keep in mind your long-term requirements to avoid regrets.
Understanding Different Types of PC Boards: A Comprehensive Overview
When selecting the right PC boards, understanding different types is crucial. There are several categories to consider. For example, there are single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. Each type serves unique functions and has its own specifications. Single-sided boards are typically simpler. Double-sided allows for more complex connections. Multi-layer boards are more advanced, often used in high-tech applications.
Choosing the right board is not just about type. Think about the purpose. What will it be used for? This decision impacts the material and size. Also, consider your budget. Cheaper options might seem enticing but can lead to issues. Sometimes, higher cost boards offer better durability and performance.
Here are some tips to guide you. Research the specific requirements of your project. Always align the board's capabilities with your project goals. Additionally, consult with experts or join forums for insights. Don't hesitate to ask questions. This can shed light on aspects you may overlook. Take your time to analyze your choices. A hasty decision can lead to frustrations later.
Top Tips for Choosing the Right PC Boards for Your Needs
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting PC Boards for Your Projects
When selecting PC boards for your projects, consider compatibility with your components. Ensure that the board has the right layout for the parts you will use. Measuring the dimensions and checking pin configurations can save time later. It is essential to match the board's specs with your project's needs.
Material choice is another critical factor. Different materials can affect performance and durability. For instance, FR-4 is common, but some projects may require specialized substrates. These choices can influence cost and lead times, so weigh your options carefully. Reflect on how material choices align with your project goals. Every detail matters.
Power requirements should not be overlooked. Assess the voltage and current needs of your components. Some boards may not handle high power efficiently. This oversight can lead to failures down the line. Take time to evaluate the power handling capabilities of the board you consider. It’s easy to assume all boards are equal, but they are not.
The Role of Material in PC Board Performance: Exploring Options and Specs
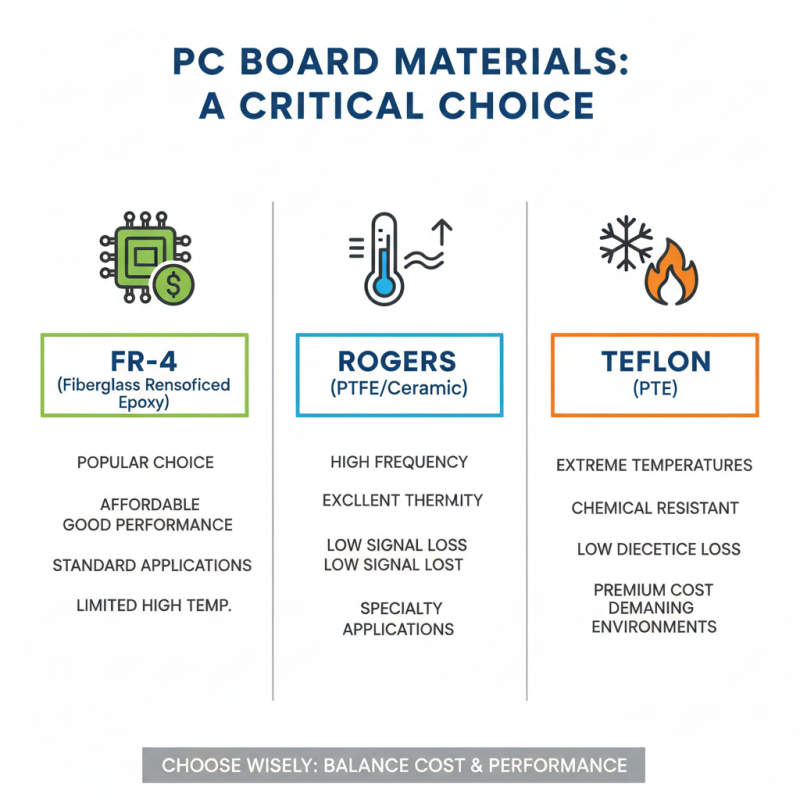
When selecting PC boards, material choice is crucial. Different materials offer various benefits. For example, FR-4 is popular for its balance of affordability and performance. However, it might not withstand extreme temperatures. Alternatives like Rogers or Teflon provide better thermal stability but come at a higher cost. Each material has a unique set of properties, impacting overall board performance.
Think about your specific requirements. If high-frequency applications are involved, using a low-loss material is essential. Some users might overlook this aspect and face performance issues later. On the other hand, for standard applications, a typical fiberglass board may suffice. It’s essential to evaluate both current and future needs, as this can save money over time.
Certain materials require special handling processes. For instance, using polyimide can complicate manufacturing but offers excellent flexibility. Users should weigh the pros and cons carefully. The right material can enhance the board's durability and efficiency. A thoughtful approach to selection will address many potential challenges. Thus, evaluating material options is vital for optimal PC board performance.
Evaluating PCB Manufacturing Techniques: Cost, Quality, and Turnaround Time
When evaluating PCB manufacturing techniques, cost becomes a significant factor. Lower costs may seem appealing, but they can lead to compromised quality. Many manufacturers offer cheap prices, but use subpar materials. This can result in unreliable products that fail prematurely. Always analyze the detailed quotes provided by manufacturers. Understand what is included in the price.
Quality is critical in PCB production. Ensure the manufacturer adheres to established standards. Look for certifications that can offer assurance about their processes. Sometimes, higher quality entails a higher price. However, saving money upfront may lead to future losses. Evaluating the quality of the service can save headaches later.
Turnaround time is another essential aspect. A quick turnaround can be beneficial, especially in fast-paced projects. However, it is important to ensure that quality is not sacrificed for speed. Some manufacturers might promise fast delivery but fail to deliver quality boards. Regularly communicate with your chosen manufacturer. It helps to clarify expectations and timelines; setting clear deadlines can help avoid misunderstandings.
Top Tips for Choosing the Right PC Boards for Your Needs
| PCB Type | Manufacturing Technique | Estimated Cost ($) | Quality Rating (out of 10) | Turnaround Time (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided PCB | Traditional Etching | 50 - 100 | 8 | 5 |
| Double-Sided PCB | Laser Direct Imaging | 100 - 200 | 9 | 7 |
| Multi-layer PCB | HDI Technology | 200 - 500 | 10 | 10 |
| Flexible PCB | Surface Mount Technology | 100 - 300 | 9 | 15 |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Integrated Circuit Assembly | 300 - 600 | 10 | 20 |
Industry Standards and Compliance: Ensuring Your PCB Meets Regulatory Needs

When selecting the right printed circuit boards (PCBs), understanding industry standards and compliance is crucial. With the electronics market expected to grow by 5% annually, adhering to regulations shapes product acceptance. Compliance with standards like IPC-2221 can enhance the reliability of your PCB. A report by the IPC found that up to 30% of boards fail to meet these standards, leading to significant costs.
Ensuring your PCB design meets regulatory needs involves several aspects. RoHS compliance is a prime example. This directive restricts harmful substances in electrical and electronic equipment. An alarming 20% of manufacturers still do not fully comply, raising serious sustainability concerns. Companies must prioritize environmental impact alongside quality.
Moreover, certification can vary widely by region. Some areas may have additional local regulations that complicate matters. The chaos in understanding these differences often leads to mistakes. Shows that 15% of PCB designs overlook necessary compliance checks, risking product recalls. This oversight can endanger a company's reputation and finances. Striving for clarity in these regulations is not just beneficial; it is essential.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 PC Boards for Optimal Performance in 2023
-
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development
-
Top Circuit Boards Technologies Transforming Electronics Today?
-

Top 10 Best Printed Circuits Designs for Electronics in 2023
-
How Printed Circuit Boards Shape the Future of Technology with Insights from Industry Trends
-

Top 10 Printed Boards: Best Options for Quality and Performance in 2023