What is a Flex Circuit? Benefits, Applications, and Key Considerations Explained
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, the significance of flex circuits cannot be overstated. A flex circuit, or flexible printed circuit board, is designed to be lightweight, adaptable, and efficient, making it an essential component in various industries, from consumer electronics to medical devices. According to Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in electronic engineering, "Flex circuits are revolutionizing the way we design and integrate components, enabling us to create more compact and robust devices."
These innovative circuits allow for greater design freedom and improved reliability, as their flexibility accommodates intricate layouts and reduces the risk of mechanical failure. As technology continues to advance, the demand for flex circuits is steadily increasing, prompting manufacturers to explore new applications and optimization techniques. This introduction not only highlights the fundamental benefits and applications of flex circuits but also sets the stage for a deeper understanding of the critical considerations businesses must take into account when implementing flex circuit technology in their products.

What is a Flex Circuit? An Overview of Its Definition and Purpose
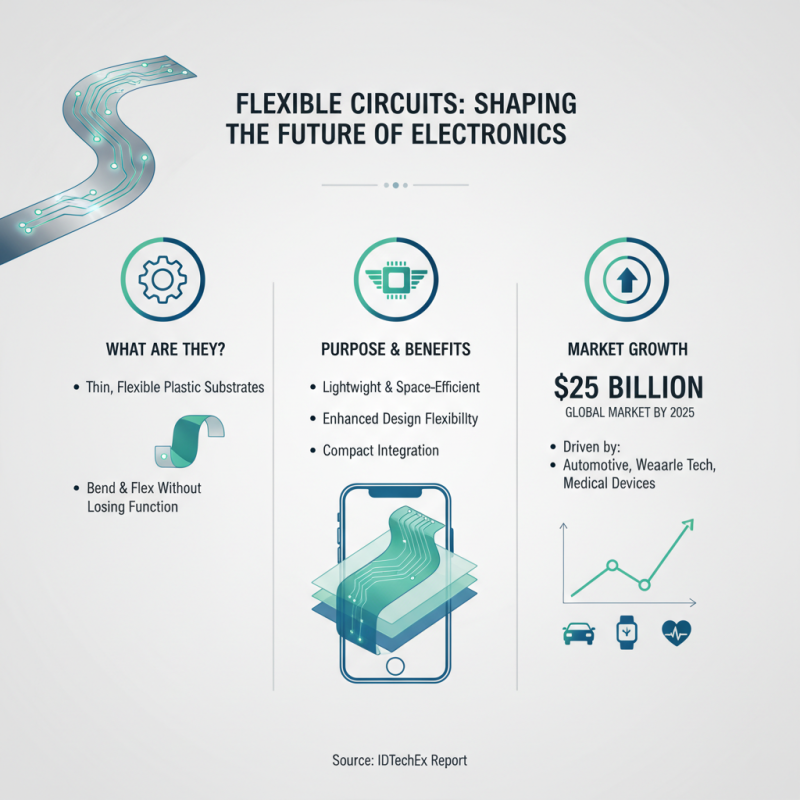
Flexible circuits, commonly known as flex circuits, are innovative electrical circuits that can bend and flex without losing their functionality. They are typically made from thin, flexible plastic substrates, enabling them to be integrated into compact and intricate electronic devices. The purpose of flex circuits is to provide a lightweight and space-efficient alternative to traditional rigid circuits, allowing for enhanced design flexibility in applications ranging from consumer electronics to medical devices. According to a report by IDTechEx, the global market for flexible circuits is projected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $25 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand in sectors such as automotive and wearable technology.
The benefits of flex circuits are manifold. Their lightweight nature reduces the overall weight of electronic assemblies, which is crucial in portable devices. Additionally, the ability to bend and conform to various shapes can lead to more efficient use of space within products, making them ideal for designs with limited real estate. Furthermore, flex circuits exhibit superior resistance to mechanical stress and vibration, enhancing durability in demanding applications. A study by Research and Markets highlights that the adoption of flex circuits in the automotive industry alone could lead to a cost reduction of up to 20% in production processes, showcasing their significant economic advantage. This innovative technology not only facilitates advanced design possibilities but also improves product reliability across diverse industries.
Key Advantages of Using Flex Circuits in Various Industries
Flex circuits, also known as flexible printed circuits, offer several key advantages that make them an attractive choice across various industries. One of the primary benefits is their ability to save space. Traditional rigid circuits often require additional support and can add bulk to designs. In contrast, flex circuits can bend, twist, and conform to the spatial requirements of compact devices, such as wearable technology and mobile electronics. This flexibility allows for more innovative product designs without compromising performance.
Another significant advantage of flex circuits lies in their durability. They are less likely to suffer from mechanical stress or damage because of their flexible nature. This attribute is particularly valuable in applications involving vibrations or movement, such as automotive and aerospace sectors. Furthermore, manufacturers appreciate that flex circuits can simplify assembly processes by reducing the number of components needed, which can also lead to cost savings.
**Tips**: When considering flex circuits for your project, assess the environment where the circuit will be used. Consider factors like temperature, exposure to moisture, and potential for mechanical stress. Additionally, collaboration with experienced manufacturers during the design phase can help optimize the circuit layout for performance and reliability.
Benefits of Flex Circuits in Various Industries
This bar chart displays the percentage of advantages that flex circuits offer across various industries. Consumer electronics show the highest advantages (75%), while the aerospace industry has comparatively lower advantages (45%). These insights highlight the growing adoption and versatility of flex circuits in modern technology applications.
Common Applications of Flex Circuits in Modern Technology

Flex circuits, also known as flexible printed circuits, have become integral to modern technology, providing versatile solutions in various applications. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global flexible printed circuit market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.17% from 2022 to 2030, driven by the increasing demand for miniaturized electronic devices. This development is particularly evident in consumer electronics, where flex circuits enable the design of compact devices without sacrificing performance.
One of the most prominent applications of flex circuits is in the automotive industry, where they are utilized in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment systems. A study published by the International Journal of Electronics highlights that the integration of flex circuits in vehicles enhances functionality while reducing weight, an essential factor for improving fuel efficiency. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles has stimulated the need for flexible electronics in battery management and monitoring systems, allowing for more efficient space utilization and enhanced thermal management.
Another significant sector benefiting from flex circuits is the medical field. The increasing prevalence of wearable health devices has accelerated the demand for flexible, lightweight electronics. According to a report by IDTechEx, the market for wearable medical devices is expected to reach $60 billion by 2025. Flex circuits not only facilitate the compact design of these devices but also enable robust performance in challenging environments, making them ideal for monitoring patient health continuously. With their ability to conform to various shapes and withstand continuous bending, flex circuits are proving essential in modern technological advancements.
Essential Factors to Consider When Designing Flex Circuits
When designing flex circuits, several essential factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Firstly, the choice of materials is critical; polyimide and polyester are commonly used substrates due to their excellent thermal and electrical properties. According to a report by the IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits), the right material selection can enhance the flexibility and durability of the circuit, which is vital for applications in confined spaces and harsh environments.
Another key consideration is the layout design, where engineers must account for the bending radius and the stress points in the circuit. A well-optimized design reduces the risk of mechanical failure. The IPC report highlights that improper layout can lead to an increased failure rate, with a significant percentage of flex circuit failures linked to design flaws.
Tip: Before finalizing your design, prototype various layouts to assess which configuration minimizes stress and maximizes performance. Additionally, utilizing simulation tools can help predict how the circuit will behave under different conditions, ultimately leading to more reliable products.
Lastly, it's crucial to consider the manufacturing process. Each production method has implications for the circuit's final properties. Data from the FlexTech Alliance emphasizes that understanding the manufacturing capabilities can help align design goals with practical production limits, ensuring a seamless transition from design to production.
What is a Flex Circuit? Benefits, Applications, and Key Considerations Explained
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Polyimide |
| Thickness | 0.1 mm - 0.2 mm |
| Layer Count | 1-6 layers |
| Bending Radius | 10 mm - 25 mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 105°C |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, Medical devices, Automotive |
| Benefits | Lightweight, Flexible, Space-saving design |
| Key Consideration | Cost, Manufacturing capabilities, Design complexity |
Comparison of Flex Circuits with Rigid Printed Circuit Boards
Flex circuits, also known as flexible printed circuits (FPCs), offer a distinct advantage over rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) in various applications. One of the primary benefits of flex circuits is their ability to bend and conform to different shapes and spaces, making them ideal for compact and lightweight devices.
According to a recent market report, the global flexible printed circuit board market is expected to reach approximately $60 billion by 2026, with a significant portion of this growth attributed to the increasing demand in consumer electronics and automotive sectors. Flex circuits can significantly reduce assembly time and enhance reliability by integrating multiple functions into a single component, which is often not feasible with traditional rigid PCBs.
In contrast, rigid PCBs present limitations in applications where space and weight are critical factors. Their inability to flex can lead to stress and potential failure in dynamic environments, which is especially pertinent in industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Moreover, while rigid circuits typically offer lower manufacturing costs for high-volume production, advances in flex circuit technology are narrowing the cost gap.
A comparative analysis indicates that while the initial investment in flex circuits might be higher, the long-term savings from reduced assembly complexity and increased product lifespan can provide robust financial benefits, contributing to their growing adoption across diverse industries. As technology continues to evolve, understanding these differences will be critical for engineers and designers in making informed decisions on circuit solutions.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using Printed PCB Boards for Your Electronics Projects
-

Mastering Circuit Board Design Fundamentals for Beginners in Electrical Engineering
-

10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs
-
Exploring the Advantages of Aluminum PCBs in Modern Electronic Design: A Complete Guide
-
Why Printable Circuit Boards are Revolutionizing Modern Electronics Design
-
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development