What is a LED Circuit Board and How Does it Work in Electronics
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, the LED circuit board has emerged as a critical component that not only enhances design but also improves energy efficiency. According to Dr. Emily Tran, a leading expert in electronic engineering, "The LED circuit board is transforming how we think about lighting and displays, serving as the backbone for innovation in various applications." This pivotal technology integrates LEDs onto a circuit board, allowing for compact designs and effective heat dissipation, which are essential features in today's high-performance devices.
The functionality of an LED circuit board is rooted in its ability to distribute electrical current across multiple LED chips, ensuring uniform brightness and prolonged lifespan. This sophisticated assembly not only supports traditional lighting functions but also plays a vital role in advanced applications such as automotive lighting, medical equipment, and interactive displays. As industries continue to demand more from their electronic components, understanding the mechanics and advantages of LED circuit boards becomes paramount for engineers and designers alike.
What Are LED Circuit Boards and Their Role in Electronics
LED circuit boards, often referred to as LED PCBs, serve a crucial role in modern electronics by providing a platform for mounting light-emitting diodes and facilitating efficient thermal management. These circuit boards are designed to accommodate the specific configurations of LEDs, enhancing light output while minimizing energy consumption. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global LED circuit board market is projected to reach USD 8.12 billion by 2026, highlighting the growing demand for energy-efficient lighting solutions across various applications, including consumer electronics, automotive lighting, and architectural designs.
The primary function of LED circuit boards is to distribute electric power to the diodes while ensuring proper heat dissipation. Typically constructed from materials with excellent thermal conductivity, like aluminum or copper, these boards help to manage the heat generated during operation, thus prolonging the lifespan of the LEDs. Moreover, innovations in LED technology, such as chip-on-board (COB) configurations, have further optimized their performance. A study by the Lighting Research Center indicates that utilizing COB designs can increase light output per watt by up to 30%, making LED circuit boards integral in advancing energy-efficient lighting solutions in the electronics sector. As the industry continues to evolve, LED circuit boards will remain a key component in driving the adoption of sustainable lighting technologies.
LED Circuit Board Usage in Different Applications
This bar chart illustrates the various applications where LED circuit boards are utilized, showcasing their significant presence in home lighting and commercial lighting, along with other areas like automotive and displays.
The Basic Structure of LED Circuit Boards: Components and Materials
LED circuit boards
are key components in modern electronic devices, providing the foundation for efficient lighting solutions. The basic structure of an LED circuit board typically involves several essential components. At its core, the substrate serves as the backbone, often made from materials like FR4, aluminum, or flexible polymers, which help with thermal management and durability.
The choice of substrate material directly influences the board's performance and longevity, particularly in high-temperature operations.
Mounted on the substrate are the LED chips themselves, which emit light when electrical current passes through them. These chips are usually arranged in specific patterns to ensure even light distribution and maximum efficacy.
Connecting these chips are conductive traces that are etched onto the surface of the board, facilitating the flow of electricity. Additional components, such as resistors and capacitors, may also be included to regulate current and improve overall performance, ensuring that the LEDs operate efficiently while prolonging their lifespan.
With careful design and material selection, LED circuit boards can meet diverse application needs,
from simple indicator lights to intricate display systems.
How LED Circuit Boards Function: Electrical and Thermal Management
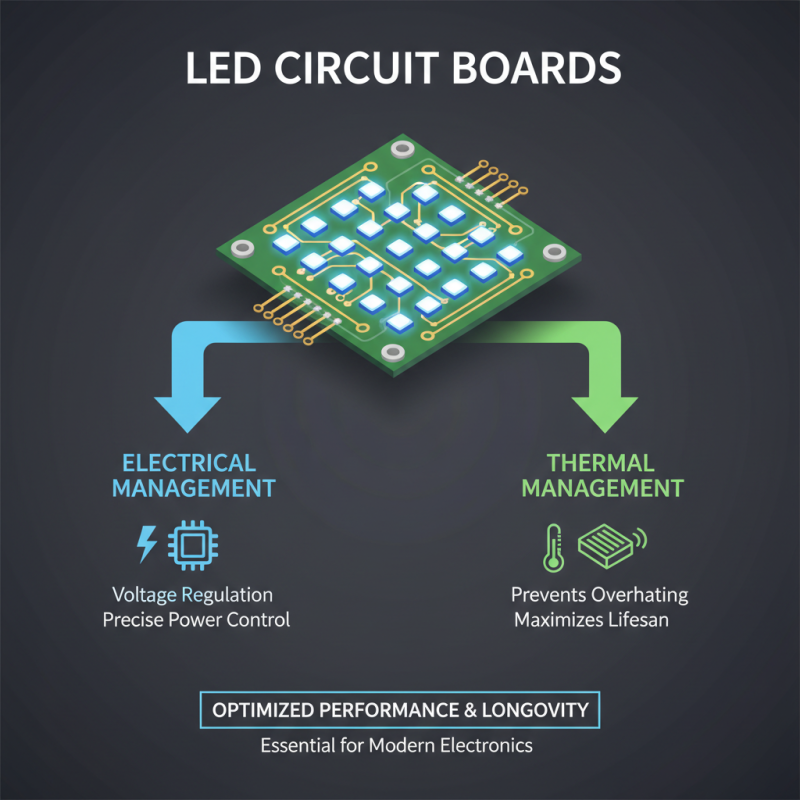
LED circuit boards are essential components in modern electronics, designed to optimize the performance and longevity of LED lighting systems. Functionality hinges on careful electrical and thermal management, which are crucial in preventing overheating and maximizing efficiency. Each LED on the circuit board is connected to a power source, allowing for precise control over the light output. Proper voltage regulation ensures that LEDs receive adequate power without exceeding their limits, thus keeping them functioning safely and effectively.
Thermal management is equally critical for the longevity of LED circuit boards. Excessive heat can degrade the performance of the LEDs, leading to reduced brightness and shorter lifespan. To combat this, many LED circuit boards incorporate thermal management techniques such as heat sinks, thermal pads, and specialized materials designed to dissipate heat. By maintaining optimal temperatures, these boards not only enhance the performance of the LEDs but also improve energy efficiency, making them a vital component in the design of sustainable lighting solutions.
Types of LED Circuit Boards: Choosing the Right Design for Applications
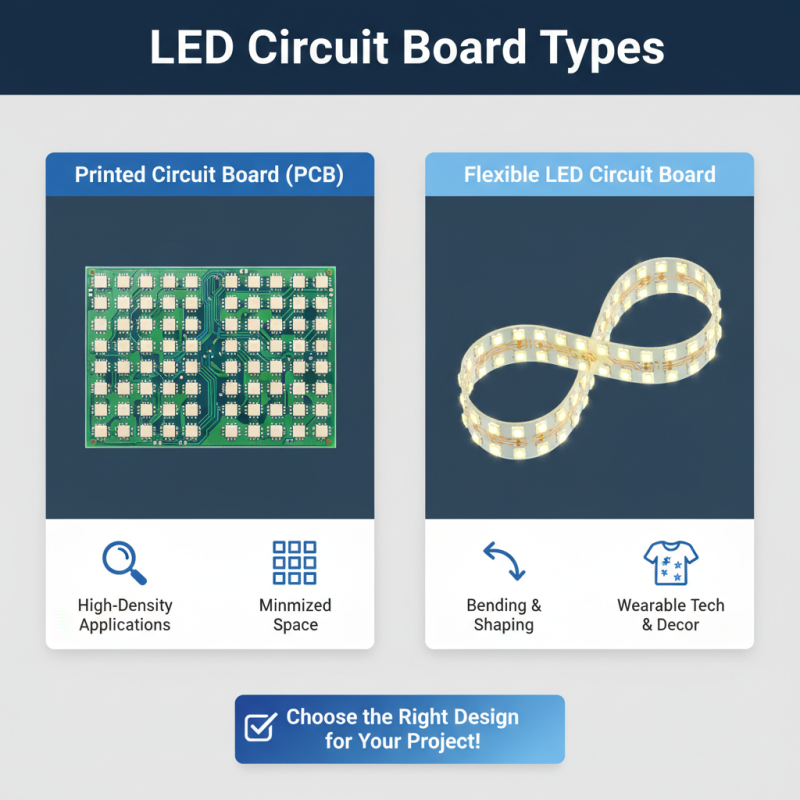
When it comes to LED circuit boards, understanding the different types available is crucial for selecting the right design for specific applications. LED circuit boards can vary significantly in terms of structure, size, and functionality, making it important to assess the requirements of your project before making a decision. For instance, a printed circuit board (PCB) may be preferred for high-density applications due to its ability to accommodate multiple LED connections with minimized space. On the other hand, flexible LED circuit boards are ideal for applications that require bending or shaping, such as in decorative lighting or wearable technology.
Moreover, the choice between single-layer and multi-layer LED circuit boards can impact the overall efficiency and performance of a circuit. Single-layer boards tend to be more cost-effective and are suitable for simpler designs, whereas multi-layer boards offer the benefits of better thermal management and reduced electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for more complex electronic applications. It’s essential to evaluate the thermal requirements, electrical properties, and mechanical constraints of the intended application to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the LED circuit board used.
Advancements in LED Circuit Board Technology: Trends and Future Outlook
The advancements in LED circuit board technology have significantly transformed the landscape of electronics, reflecting a shift towards energy efficiency and miniaturization. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global LED lighting market is projected to reach $105.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 13.5% from 2019 to 2026. This growth is driven by the move towards sustainable energy solutions and the increasing demand for smart lighting systems that integrate seamlessly with IoT devices. LED circuit boards play a crucial role in this trend, as they not only provide efficient illumination but also allow for complex interactions with smart technologies.
Moreover, as the demand for compact and high-performance devices increases, advancements in LED circuit board design have become paramount. Innovations such as flexible circuit boards and improved thermal management systems are critical for enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of LEDs. A recent study by Research and Markets indicates that the circuit board assembly market is expected to grow to $63.4 billion by 2025, with the LED segment accounting for a significant portion due to its widespread application in various sectors, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. The integration of advanced technologies like surface-mount technology (SMT) and automated assembly processes is further driving efficiency and scalability in LED production, showcasing a promising future for this dynamic sector.
What is a LED Circuit Board and How Does it Work in Electronics - Advancements in LED Circuit Board Technology: Trends and Future Outlook
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | A LED Circuit Board is a specialized circuit board designed to house LED components and connect them electrically. |
| Function | It allows for efficient electrical connections and control of LED lights, ensuring they operate correctly and reliably. |
| Material | Typically made from materials like FR-4, aluminum, or flexible substrates to handle heat dissipation and support flexibility where required. |
| Technological Advancements | Enhancements include better thermal management, higher energy efficiency, and integration with smart technologies. |
| Future Trends | The focus is on miniaturization, improved durability, and integration with IoT for smarter lighting solutions. |
| Applications | Used in various fields such as automotive lighting, consumer electronics, architectural lighting, and more. |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top Trends in Printed PCB Board Technology and Innovations You Need to Know
-

Top 10 Printed Boards: Best Options for Quality and Performance in 2023
-
Why Printable Circuit Boards are Revolutionizing Modern Electronics Design
-

10 Best PCB Flex Technologies to Enhance Your Electronic Designs
-
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development
-

Top 10 Printed PCB Board Insights: Trends, Market Value & Manufacturing Innovations in 2023