What is PCB Production and How Does it Impact Electronics Industry?
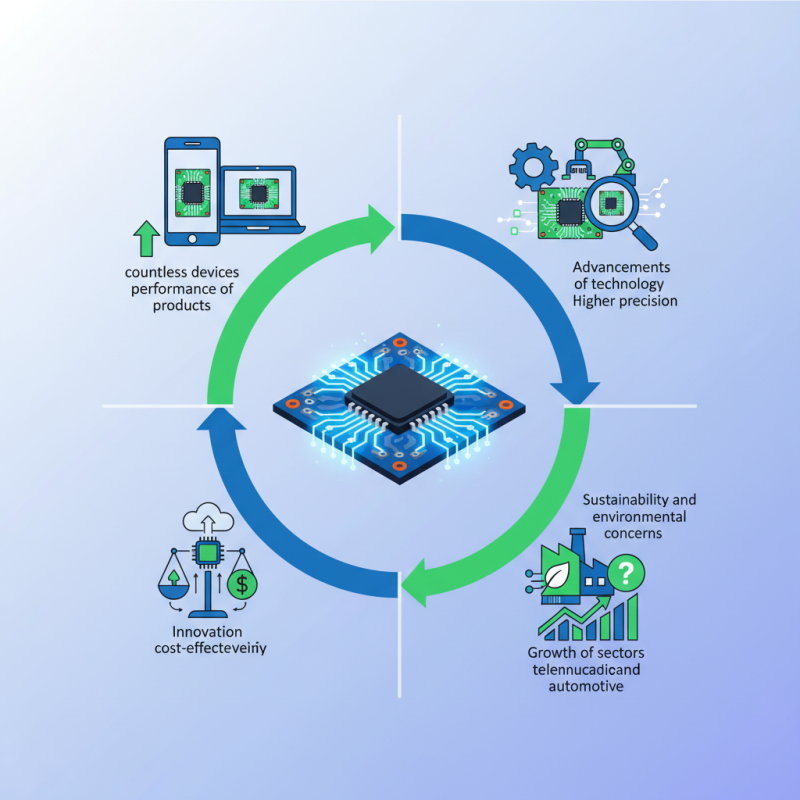
PCB production is a critical process in the electronics industry. It involves creating printed circuit boards, essential components in countless devices. The quality and efficiency of PCB production directly influence the performance of products. From smartphones to industrial machinery, PCBs form the backbone of electronic systems.
In recent years, advancements in technology have changed PCB production significantly. Manufacturers are adopting new materials and techniques, aiming for higher precision. However, this rapid evolution brings challenges too. There is pressure to keep up with innovation while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Companies must carefully evaluate their production methods.
Despite these challenges, the impact of effective PCB production cannot be overstated. It drives the growth of sectors like telecommunications and automotive. Yet, questions remain about sustainability and environmental concerns in production practices. Continuous improvement is necessary to address these issues while meeting market demands. The future of PCB production will shape the industry in exciting ways.
Understanding PCB Production: Definition and Importance
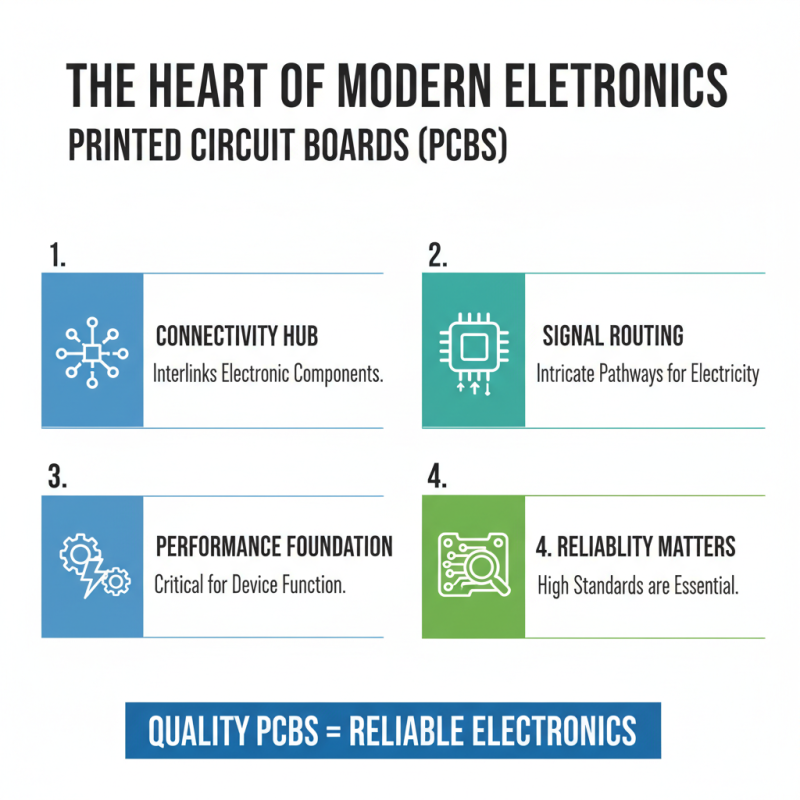
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are critical components in modern electronics. They serve as the backbone of electronic devices, allowing connections between different components. Each PCB is designed with intricate pathways that facilitate the flow of electricity. This complexity plays a key role in the device's performance. Yet, not every PCB meets the high standards required for reliability.
The accuracy of PCB production directly affects the lifespan of electronic products. Flaws in the production process can lead to malfunctions. These issues may include improper soldering or misalignment of components. Such errors can be costly, resulting in wasted resources and dissatisfied customers. It is crucial for manufacturers to prioritize quality control in this process. Attention to detail can prevent future problems.
Understanding PCB production involves recognizing its importance in the electronics industry. It's not just about assembling parts; it's about creating efficient systems. Innovation in PCB technology can enhance product performance. However, the industry must also address environmental concerns associated with production waste. Balancing efficiency and sustainability remains a significant challenge for manufacturers.
The PCB Manufacturing Process: Key Steps Involved
The PCB manufacturing process involves several key steps. Each step is crucial to ensure that the final product functions correctly in the electronics industry. One of the initial stages is design. Software tools help engineers create layouts. About 24% of PCB failures occur during this phase. Careful planning can reduce these errors.
After design, material preparation follows. The choice of materials impacts performance and reliability. High-frequency PCBs often use specific materials to minimize signal loss. Statistics show that using the wrong materials can result in up to a 30% increase in failure rates.
Fabrication is next. Here, layers are etched onto the copper-clad boards. The process requires precision; errors can lead to short circuits.
Assembly comes afterward, where components are mounted. Automated machines ensure quick placement. However, human oversight is still needed. In fact, about 10% of issues stem from assembly mistakes.
Testing is essential before products hit the market. Sometimes, products fail tests unexpectedly. This reflects the need for continuous improvement in the PCB manufacturing process. It is a complex journey, with each step presenting unique challenges.
Types of PCBs and Their Applications in Electronics
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential in modern electronics. They provide a base for mounting components like resistors and capacitors. There are various types of PCBs, each tailored for specific applications. For instance, single-sided PCBs are common in simple devices, while multi-layer boards are used in advanced gadgets.
Flexible PCBs are gaining popularity due to their adaptability. They can bend and twist, fitting into tight spaces. These boards are crucial in smartphones and wearables. Rigid-flex boards combine rigidity with flexibility, allowing unique designs in complex electronics. They require careful design and testing to ensure reliability.
Some manufacturers face challenges in PCB production. Issues like solder quality or layer alignment can arise. These may lead to device failures. It's vital to continuously refine production processes. This way, the growth and stability of the electronics industry can be secured.
Impact of PCB Quality on Electronic Device Performance
The quality of printed circuit boards (PCBs) directly affects electronic device performance. A faulty PCB can lead to device malfunctions. For instance, poor soldering can cause signal loss. This results in devices that may freeze or shut down unexpectedly.
Moreover, the thickness of the PCB material plays a vital role. Thinner boards may save space but can compromise durability. A thin board might bend or break under stress. This can lead to catastrophic failures in sensitive electronics. Manufacturers often overlook this during production.
Thermal management is another critical aspect. High-quality PCBs effectively dissipate heat. Devices that run hot can suffer from reduced lifespan. A lack of proper insulation can allow heat to damage surrounding components. This creates a ripple effect, leading to larger performance issues. Some companies still struggle to balance cost and quality in their PCB production. This raises questions about their commitment to reliability.
Future Trends in PCB Technology and Their Industry Implications
The landscape of PCB technology is rapidly evolving. This shift is driven by the increasing demand for smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices. As we look ahead, several trends are reshaping the PCB industry. Innovations like flexible PCBs allow for compact designs, enabling integration into wearables and IoT devices. These advancements present both exciting opportunities and challenges.
Another emerging trend is the push for sustainable materials. Environmental concerns are prompting manufacturers to explore alternatives to traditional materials. Biodegradable substrates are gaining attention. However, developing such materials is complex and requires significant investment. The transition is not straightforward, as manufacturers weigh cost-effectiveness against sustainability.
Moreover, the rise of 5G technology is influencing PCB design. Increased frequency requires PCBs that can handle higher speeds without compromising performance. Designers face the challenge of balancing miniaturization with thermal management. Innovations in thermal conductive materials are part of the solution, but further research is needed. The industry must navigate these trends while ensuring quality and reliability remain top priorities.
Future Trends in PCB Production and Their Impact on the Electronics Industry
The chart above illustrates the projected growth of the global PCB market from 2019 to 2024. It highlights the increasing demand and technological advancements in PCB production, which significantly impacts the electronics industry by enabling the development of more sophisticated electronic devices.
Related Posts
-

Why Understanding PCB Production is Essential for Modern Electronics
-
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development
-

Top 10 Tips for Efficient PCB Creation: Boost Your Design Skills Today!
-
2026 Best PCB Prototyping Techniques for Efficient Product Development
-

Top 10 PCB Fast Manufacturing Techniques to Improve Efficiency?
-
2025 Strategies for PCB Prototyping to Improve Product Development Efficiency